
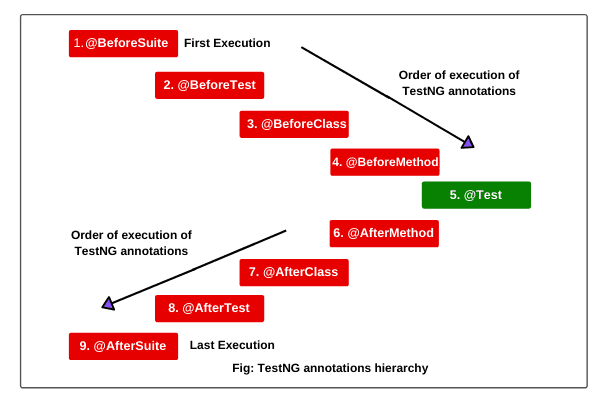
So, how will TestNG figure out which test case to run first and then the next and so on? The answer is a hierarchy in these annotations.
TESTNG ANNOTATIONS CODE
TestNG provides many annotations to write good test source code while testing software. So before we jump onto the coding part, let's see the hierarchy of these annotations. For this, we must know what test will execute first and what next. But hey!, as I said, you control the flow of the program using these annotations. Now that we know the benefits and the annotations used, its time to use them in our code.
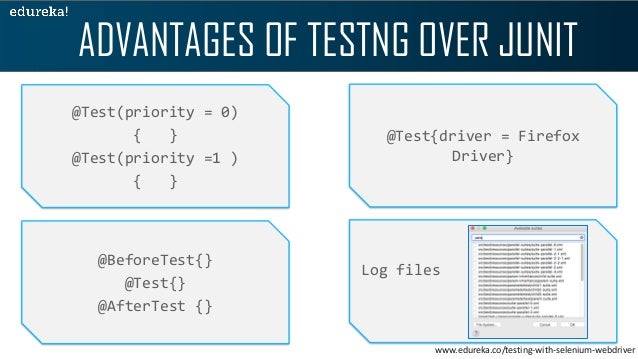
It is one of the primary reasons to prefer TestNG as it is simple and easy to learn. These annotations have self-explanatory meanings. - The method in TestNG run after the test cases of that group execute.- The method in TestNG run before the test cases of that group execute.- The method in TestNG will run after each test method is executed.- The method in TestNG will execute before each test method.- The method in TestNG will execute after all the test methods of the current class execute.- The method in TestNG will run before the first method invokes of the current class.- The method in TestNG executes after the execution of all the test methods that are inside that folder.- The method in TestNG runs before the execution of all the test methods that are inside that folder.- The method in TestNG runs after the execution of all other test methods.- The method in TestNG runs before the execution of all other test methods.In TestNG, there are ten types of annotations: In the section, you will find their definition along with their meaning. There are many types of annotations in TestNG. Apart from the ' symbol and the header file ( of course), there is nothing you require to run TestNG annotations. These names are predefined, and we will discuss them in the later section of this tutorial. TestNG will ignore the method which does not contain an annotation since it won't know when to execute this method.Ī TestNG annotation starts from the symbol " and whatever follows is the annotation name. It is essential to annotate your methods in TestNG to run the tests. TestNG annotations are the code that is written inside your source test code logic to control the flow of the execution of tests. TestNG also uses them for the same reason. This tutorial includes the TestNG Annotations with the following content:Īnnotations, in general, mean " a comment" or " a note" on a diagram, etc.

Annotations are taken from the Java language and are an excellent tool for the testers using TestNG. Tests annotate to decide the sequence of the tests that run.
return maxList.remove(maxList.In the introduction to the TestNG tutorial, we highlighted TestNG briefly and focussed on how TestNG fetches its power from its annotations. Int popVal = integerList.remove(integerList.size()-1) ĬurrentMax = maxList.get(maxList.size() - 1) I'm new to TestNG notations, can anyone help me with how can I write down TestNG test cases (testing annotations like before test, before method, before class, after class) for the following code.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
